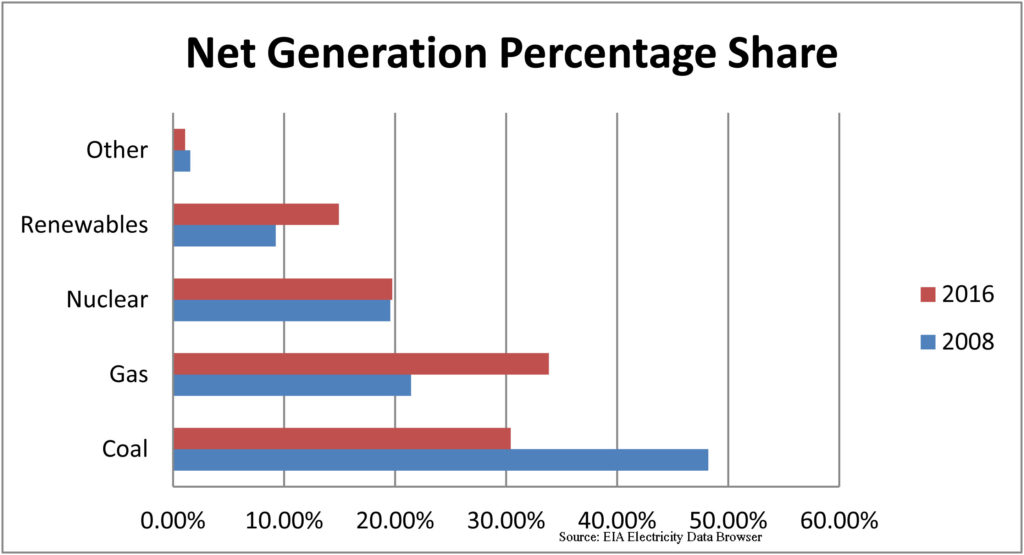
The Trump administration’s obsession with the coal industry has driven many of its early energy and environmental policy initiatives—with the Energy Department’s thinly veiled baseload power plant review just the latest in a string of efforts to buttress the troubled sector. But none of these policies are going to change coal’s central problem: The utility industry, far and away its largest customer, is steadily moving away from the black rock. This transition won’t happen overnight, but the direction is clear, as a close review of recent utility executive statements and company publications clearly demonstrates.
Consider the message delivered by Allen Leverett, president and CEO of Milwaukee-based WEC Energy Group, in the company’s latest annual report:
“I also believe that some form of carbon emission regulation is ultimately inevitable. As the regulation of carbon emissions takes shape, our plan is to work with our industry partners, environmental groups and the state of Wisconsin to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by approximately 40 percent below 2005 levels by 2030.
“In 2016, about half of the electricity we delivered to our customers was derived from low- or no-carbon sources such as natural gas, nuclear fuel, wind farms and hydroelectric facilities. However, we want to continue to make progress in this area. Relatively flat electricity demand growth, coupled with natural gas and coal economics, has driven us to re-evaluate our generation portfolio. Taken as a group, I want any changes that we make to reduce costs, preserve fuel diversity and keep us on a path to reducing our carbon emissions.”
In other words, there will be no new coal generation in the WEC fleet, and the company’s reliance on the fuel, currently around 50 percent of its needs, is going to drop. In particular, the company has plans to build new natural gas-fired generation in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan and close its five-unit, 359 megawatt Presque Isle facility there, which now burns roughly 1.2 million tons of coal annually according to the company, whose two electric utility subsidiaries serve more than 1.5 million customers in Wisconsin and the UP of Michigan.
Or consider the comments made by Lynn Good, chairman, president and CEO of Duke Energy, during the Charlotte, N.C.-based company’s annual meeting earlier this month:
“By retiring coal plants and bringing on more natural gas and renewables, we have already reduced our carbon emissions by nearly 30 percent since 2005. Today, we are among the top five companies in terms of renewable capacity, and we are committed to doing more.
“We have set a new goal to reduce our carbon emissions by 40 percent from the 2005 level by 2030.”
Continue reading Trump Coal Obsession
Largely Irrelevant
To Electric Utility CEOs
 Follow
Follow